Nasko N-PRYSM for
N-PRYSM is a realtime resynthesizer that uses a filterbank to drive tuned sine oscillators, allowing for polyphonic tuning of any sound.
N-PRYSM uses a realtime processing approach to resynthesis by splitting a specified frequency range into a filterbank that then modulates sine oscillators to resynthesize the frequency area. This allows N-PRYSM to retune, pitch shift, and lock incoming frequencies to any scale.
This PLUGDATA-FX Patch uses hundreds of filters with a latency of ~6ms. It uses downsampling techniques to drastically improve cpu performance and the dsp has been tuned carefully to offer best performance to quality ratio.
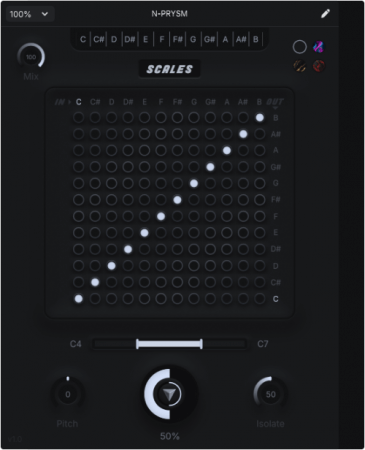
First, the MATRIX.
This is the heart of N-PRYSM and allows you to remap incoming frequencies/notes to any other note inside an octave. It does this for every octave throughout the specified frequency area.
You can manually set and automate the rows.
Matrix works as follows:
Left > right equals input note, so C-B.
Bottom > Up equals output note, so C-B.
You can also select from a few scale presets that work well in most scenarios.
The very top row with the black background sets the ROOT NOTE, which offsets the matrix to start from the selected note.
Next, the AMOUNT.
N-PRYSM uses transient splitting derived from the filterbank to decide between NOISE and TONAL content. The main dial Adjusts this ratio, with 0% considering the incoming signal as pure Noise, and 100% as pure TONAL.
For signals with transients or a lot of noise, it is recommended to find a good middleground, while softer and purely tonal signals should use the dial at 100%.
For further mixing possibilities, you can use the MIX dial found on the top left of the UI.
Now, the RANGE.
Harmonically important content is often in the mid frequencies, which is where N-PRYSM is designed to work best. The range limiter lets you select the frequency region that is supposed to be resynthesized, with a range of up to 7 OCTAVES, going from 65hz to 8500hz. The bigger the range, the more cpu will be used, as N-PRYSM dynamically disables unused parts of the filterbank.
You can grab the left and right handles to adjust the lower and upper range. Dragging from the middle of the two handles lets you move the total range left and right.
The displayed notes to the left and right of the slider ui are representative of the minimum and maximum frequencies.
Lastly, Pitching and Isolating.
N-PRYSM let's you pitch shift the filterbank by offsetting their set frequencies, resulting in a pitch shift that respects the matrix tuning you are using. This is unique to N-PRYSM and incredibly powerful.
One potential downside of N-PRYSM is the use of realtime minimum phase filters, which can cause their own noisefloor/decay as they introduce post-ringing and resonance.
This can be addressed with the ISOLATE dial, which acts as a per-oscillator noise gate, cutting off tails and potentially unwanted resonances. Note that ISOLATE can also be used creatively!
Home page
DOWNLOAD
